A few days ago, the release of the Ubuntu 24.04 Noble Numbat distribution finally appeared. Its distinctive feature is its long support period. Updates will take 12 years to form, which is quite a lot. Details are under the cut.

What's new in this release?
Many things , including updating the desktop to the release of GNOME 46. The developers did their best by adding a global search function, improving the performance of the file manager and terminal emulators, adding experimental support for the VRR (Variable Refresh Rate) mechanism, improving the output quality with fractional scaling, expanding the ability to connect to external services , updating the configurator and improving the notification system. In addition, GTK uses a new rendering engine, which is based on the Vulkan API.
Accordingly, the Linux kernel has been updated to version 6.8.
Very important changes - with the installer. It has been modernized and is being developed as a component of ubuntu-desktop-provision and renamed ubuntu-desktop-bootstrap. The main task in this case is to divide the installer into stages that are implemented before the actual installation. We are talking about partitioning the disk and copying packages during the first boot of the system and its initial setup. The installer was written in Dart, Flutter was used for the user interface. Well, the implementation is based on the low-level curtin installer, which is already used in the Subiquity installer used in Ubuntu Server. It is also worth mentioning the optimization of the interface, adding a page to indicate the download URL of the automated installation script. It is also possible to change the default behavior and design style - all through a configuration file. The minimal installation mode is also used. Well, to add programs like LibreOffice and Thunderbird you need to select the advanced installation mode.
We must not forget about the subsystems - Mesa 24.0.3, systemd 255, BlueZ 5.72, Cairo 1.18, NetworkManager 1.46, Pipewire 1.0.4, Poppler 24.02, xdg-desktop-portal 1.18.
Due to security issues, it was decided to remove packages such as pptpd and bcrelay, as well as the PAM module pam_lastlog.so, which does not solve the 2038 problem.
By default, compiler options are enabled when building packages. This is necessary to improve security—to make it more difficult to exploit vulnerabilities. In gcc and dpkg, a mode such as "-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=3" is enabled. It detects possible buffer overflows when executing string functions that are defined in the string.h header file. Previously, the "_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2" mode was used; the difference from it is additional checks. In general, they can degrade performance, but this is unlikely, and there are no user complaints about this problem.
Another important update is a change in priority in the APT package manager. Thus, the priority for the “proposed pocket” repository has now been changed, in which preliminary testing of new versions of packages is carried out. This change is intended to reduce the likelihood of unstable updates being automatically installed if the "proposed pocket" repository is enabled. Well, after activating this repo, all updates will not be transferred from it; instead, the user will be able to selectively install updates for the required packages using the command "apt install <package>/<release>-proposed".
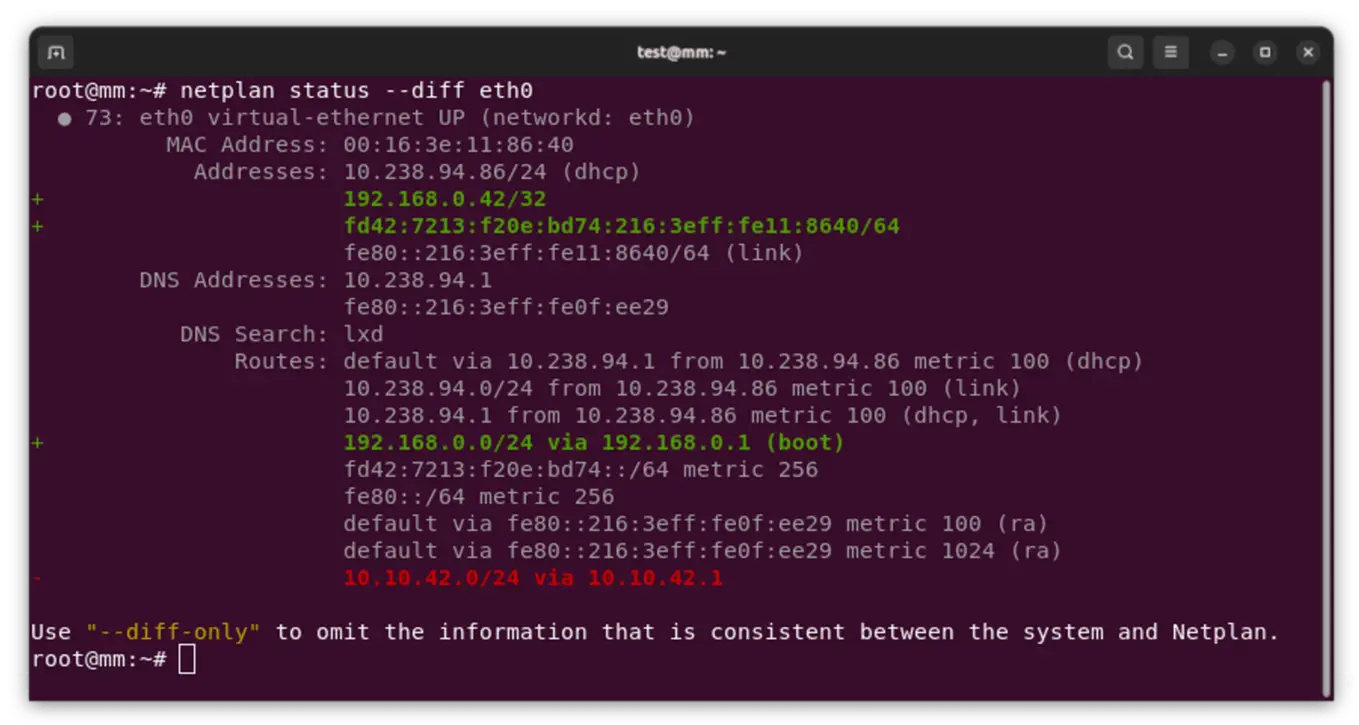
As for network configuration, the developers decided to use the Netplan 1.0 release of the toolkit, which provides storage of settings in YAML format and provides backends. It abstracts configuration access for NetworkManager and systemd-networkd. The new version now has the ability to use WPA2 and WPA3 simultaneously, adds support for Mellanox VF-LAG network devices with SR-IOV (Single-Root I/O Virtualization) and implements the “netplan status --diff” command. It is needed to visually assess the differences between the actual state of the settings and the configuration files.
Another important update is the improvement of the new application manager, which is written in the Dart language using the Flutter framework and adaptive interface layout methods to work correctly on screens of any size. Its difference is a combined interface for working with packages of different formats. It allows you to search the package directory, manage installation, update applications, and install individual packages from local files. There is also a rating system. A new interface for updating firmware has also been added, this is Firmware Updater, which is available for systems based on amd64 and arm64 architectures.
In addition, the most important server packages have been updated, including Nginx 1.24, Apache httpd 2.4.58, Samba 4.19, Exim 4.97, Clamav 1.0.0, Chrony 4.5, containerd 1.7.12, Django 4.2.11, Docker 24.0.7, Dovecot 2.3. 21, GlusterFS 11.1, HAProxy 2.8.5, Kea DHCP 2.4.1, libvirt 10.0.0, NetSNMP 5.9.4, OpenLDAP 2.6.7, open-vm-tools 12.3.5, PostgreSQL 16.2, Runc 1.1.12, QEMU 8.2 .1, SpamAssassin 4.0.0, Squid 6.6, SSSD 2.9.4, Pacemaker 2.1.6, OpenStack 2024.1, Ceph 19.2.0, Openvswitch 3.3.0, Open Virtual Network 24.03.
Another important change is that now the sysctl vm.max_map_count parameter, which determines the maximum number of memory mapping areas available to a process, has been increased by default from 65,530 to 1,048,576. This change is important because it improves compatibility with Windows games that run via Wine. Now, as far as we know, DayZ, Hogwarts Legacy, Counter Strike 2, Star Citizen and THE FINALS are launching. So there are more games, which is great.
Other updates: GCC 14-pre, LLVM 18, Python 3.12, OpenJDK 21 (OpenJDK 8, 11 and 17 are optionally available), Rust 1.76, Go 1.22, .NET 8, PHP 8.3.3, Ruby 3.2.3. The following applications were also updated: Firefox 124 (built with Wayland support), LibreOffice 24.2, Thunderbird 115, Ardour 8.4.0, OBS Studio 30.0.2, Audacity 3.4.2, Transmission 4.0, digiKam 8.2.0, Kdenlive 23.08.5, Krita 5.2.2.
Added support for various hardware and architectures. Thus, support for the QAT (QuickAssist Technology) accelerator built into Intel processors has appeared. Updated assemblies for Raspberry Pi 5 (server and user) and StarFive VisionFive 2 (RISC-V) boards.
Software has appeared for performance analysis, process tracing and system health monitoring. In particular, the procps, sysstat, iproute2, numactl, bpfcc-tools, bpftrace, perf-tools-unstable, trace-cmd, nicstat, ethtool, tiptop and sysprof packages have been added, which are combined into the performance-tools meta-package, which may be useful to many of us.
The work of the energy profile manager has also been improved. The developers have added new hardware power management mechanisms that are available in AMD chips. It is now possible to work with different optimization drivers.

